Post Processing
Post-processing is an essential step in the 3D printing workflow to ensure that the printed parts achieve the desired final quality and functionality. The specific post-processing steps can vary based on the 3D printing technology used, the material of the printed part, and the desired finish.
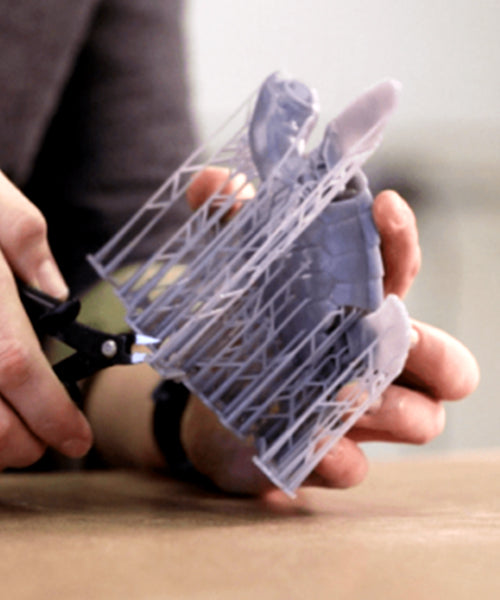
1, Support Removal
Support removal is a crucial post-processing step for many 3D printing technologies, particularly Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) and Stereolithography (SLA) printing. Supports are structures added to the print to provide stability for overhanging features during the printing process.


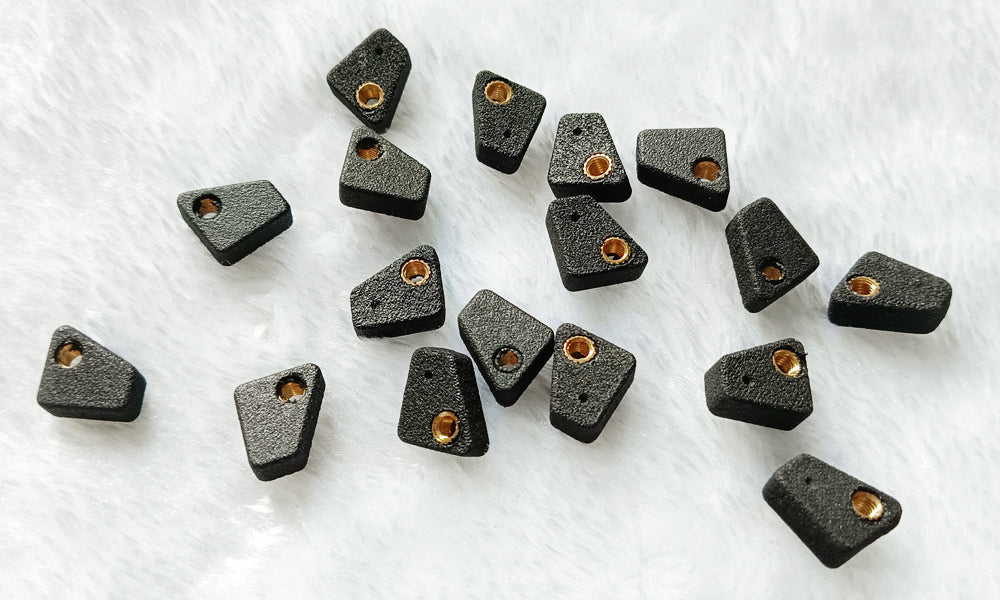
2, Inset Screw Nut Or Tap Thread
Inserting screw nuts or tapping threads into 3D printed parts is important for:
- Making strong connections with screws or bolts.
- Allowing easy assembly and disassembly.
- Creating a seamless design without visible screws.
- Providing customization for specific screw sizes.
- Saving space and reducing weight in the design.

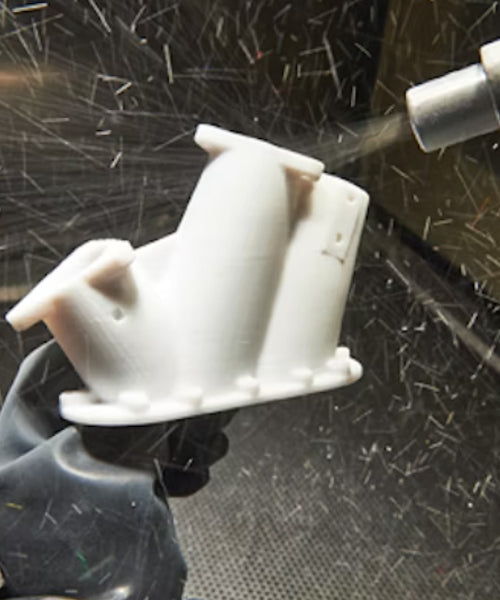
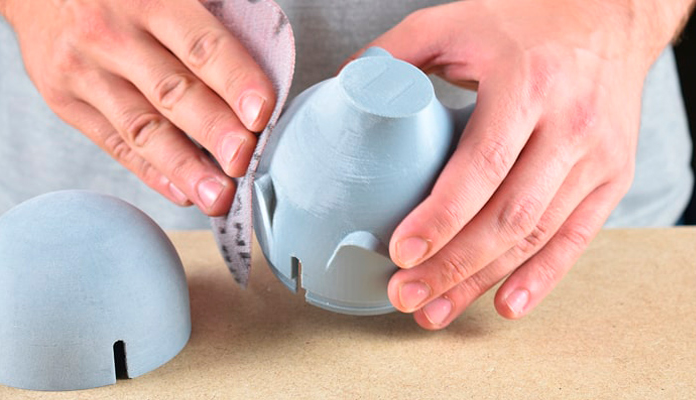
3, Sanding and Polishing
Sanding is often used to smooth rough surfaces and remove imperfections.
After sanding, polishing compounds or processes can be used to bring the surface to a higher gloss. This is particularly common for resin prints.


-

Model without polishing
The non-polishing model will come with layer lines or scatch.
-

Model with polishing
The surface of the model is smooth, comes without layer lines or scatch.
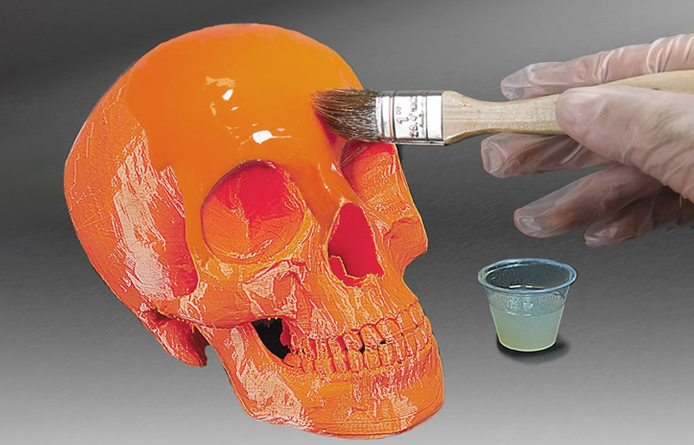
4, Painting and Coating
Many 3D-printed parts are painted or coated for aesthetics or functionality. This can include spray painting, airbrushing, or applying specialized coatings for protection or specific properties


5, Assembly
3D printing splicing typically refers to the process of combining or connecting multiple 3D printed parts or components to create a larger or more complex object. This technique is often used when the size of the intended print exceeds the build volume of the 3D printer, or when it's more efficient to print a design in separate parts for assembly.
6, Water transfer printing
- Water transfer printing, also known as hydrographic or hydro dipping, is a post-processing technique used to apply intricate and customized designs, patterns, or images to the surface of 3D-printed objects.
- Water transfer printing is commonly used in automotive, consumer electronics, sporting goods, and various other industries to decorate and customize products. In 3D printing, it can be applied to a wide range of objects, including phone cases, automotive parts, home decor, and more.
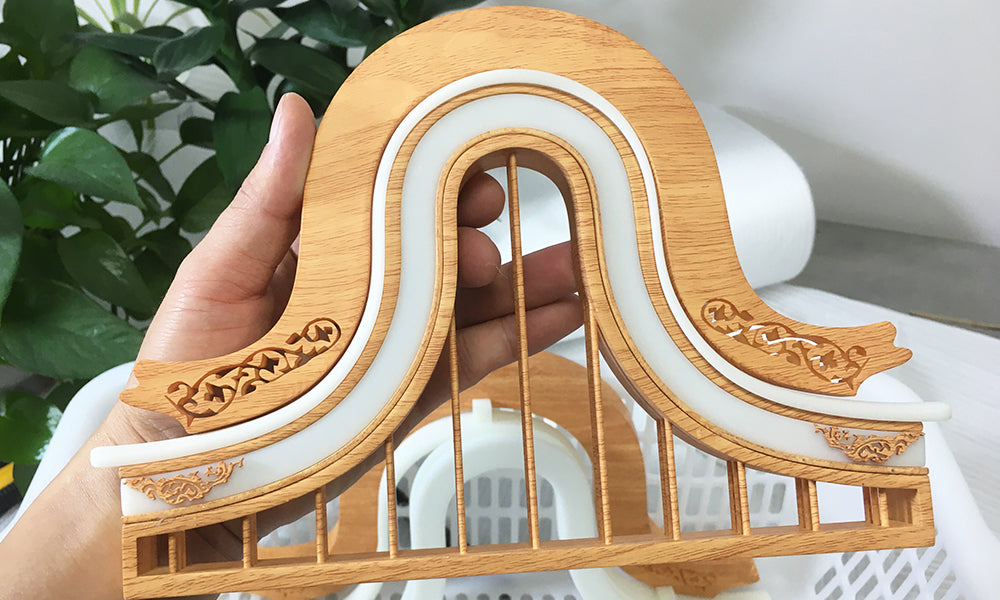



7, Silk Screen
- Silk screen, also known as pad printing or tampography, is a post-processing technique used to apply designs, logos, or markings onto the surface of 3D printed objects.
- Silk screen printing is widely used in various industries, including consumer goods, automotive, electronics, promotional products, and more. In 3D printing, it can be applied to customize products, industrial parts, promotional items, and consumer electronics, among others.
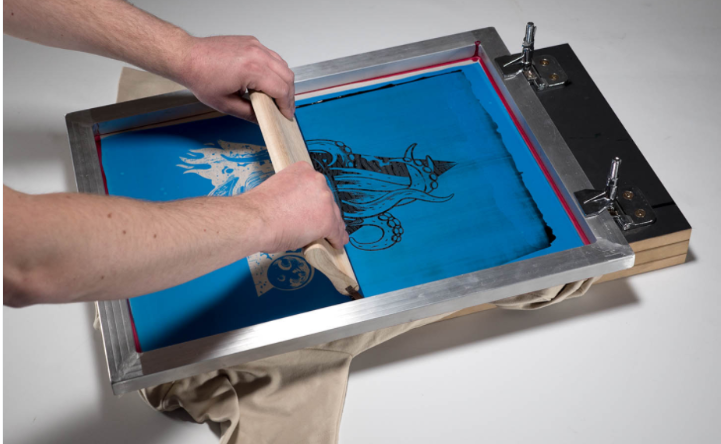


8, Laser carving
- 3D printing parts laser carving, also known as laser engraving or laser etching, is a post-processing technique used to mark, carve, or engrave designs, patterns, or information onto the surface of 3D printed objects.
- Laser carving on 3D printed parts is used to mark, label, personalize, or add aesthetic designs to the surface of the objects. It offers a precise and permanent way to customize 3D-printed items.
- Laser carving is widely used in various industries, including electronics, jewelry, awards and plaques, signage, and promotional items. In 3D printing, it can be applied to personalize consumer products, industrial parts, awards, and decorative items.
9, Chrome Treatment
3D printing parts plating, also known as electroplating, is a post-processing technique used to apply a thin layer of metal onto the surface of 3D printed objects. This process involves the application of an electric current to deposit metal ions onto the surface of the printed part, resulting in a plated or coated finish.
Plating serves multiple purposes, including enhancing the appearance, providing better corrosion resistance, improving conductivity, or achieving a specific surface finish for 3D-printed objects.
- Product Applications:
- Plating is widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, jewelry, and consumer goods. In 3D printing, it can be applied to parts that require a metallic finish, improved electrical conductivity, or enhanced durability.
- Plating 3D printed parts enables the creation of objects with a metallic appearance, enhanced functionality, and improved properties, making them suitable for a variety of applications and industries.
10, Anodizing
- Anodizing is a surface treatment process used to create a protective oxide layer on the surface of metals, typically aluminum.
- Anodizing serves several purposes, including enhancing the metal's corrosion resistance, improving its durability, and providing an attractive surface finish.
- The oxide layer formed through anodizing can also act as a base for additional processes like dyeing or sealing.









